Welcome to iNuLoC
Many proteins shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm in response to various signals and regulate a broad spectrum of biological processes. This dynamic transport process is mediated by the nuclear location signal (NLS) and nuclear export signal (NES).NLS/NESs have been experimentally determined for fewer than 10% of known nuclear proteins, the majority of proteins do not have known or potential NLS/NES annotation. Here we developed a deep learning-based model to predict the nuclear location proteins, discovered complex biological rules to decipher protein nuclear location potential. Further, we developed iNuLoC to reveal the candidate regions that may be critical for protein nuclear localization.
iNuLoC is a platform developed for understanding potential critical regions that facilitate the protein nuclear location for five model organisms. It provides the prediction results of pNuLoC and integrates several well-known database including UniProt, NLSdb, SeqNLS, ValidNESs and NESbase to display known and candidate NLSs/NESs in the proteins, which might provide helpful information for the research of protein nuclear location. In total, the platform contains experimentally determined NLS/NESs for 1,530 proteins through database integration. Using ‘Nuclear Location Probability Trajectory Method’, the NLS/NES annotations were extended to 13,481 proteins and the final dataset matched over 93% of all known nuclear proteins. The platform also contains 14,585/23,208/27,551 predicted nuclear proteins for the proteomes of five model organisms with High/Medium/Low thresholds.
The deep learning model to establish iNuLoC, namely pSAM (Prediction of Shuttling-Attacking Mutations), could also be found at GitHub Repository (https://github.com/zhengyq1/pSAMmodel/).

• iNuLoC displays the prediction results of pNuLoC, which contains the probability of protein nuclear location and the potential critical region.
• Several databases with known and potential NLS/NES information were integrated into iNuLoC.
• iNuLoC contains all proteins of five model organisms, including Homo sapiens, Rattus norvegicus, Mus musculus, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Drosophila melanogaster.
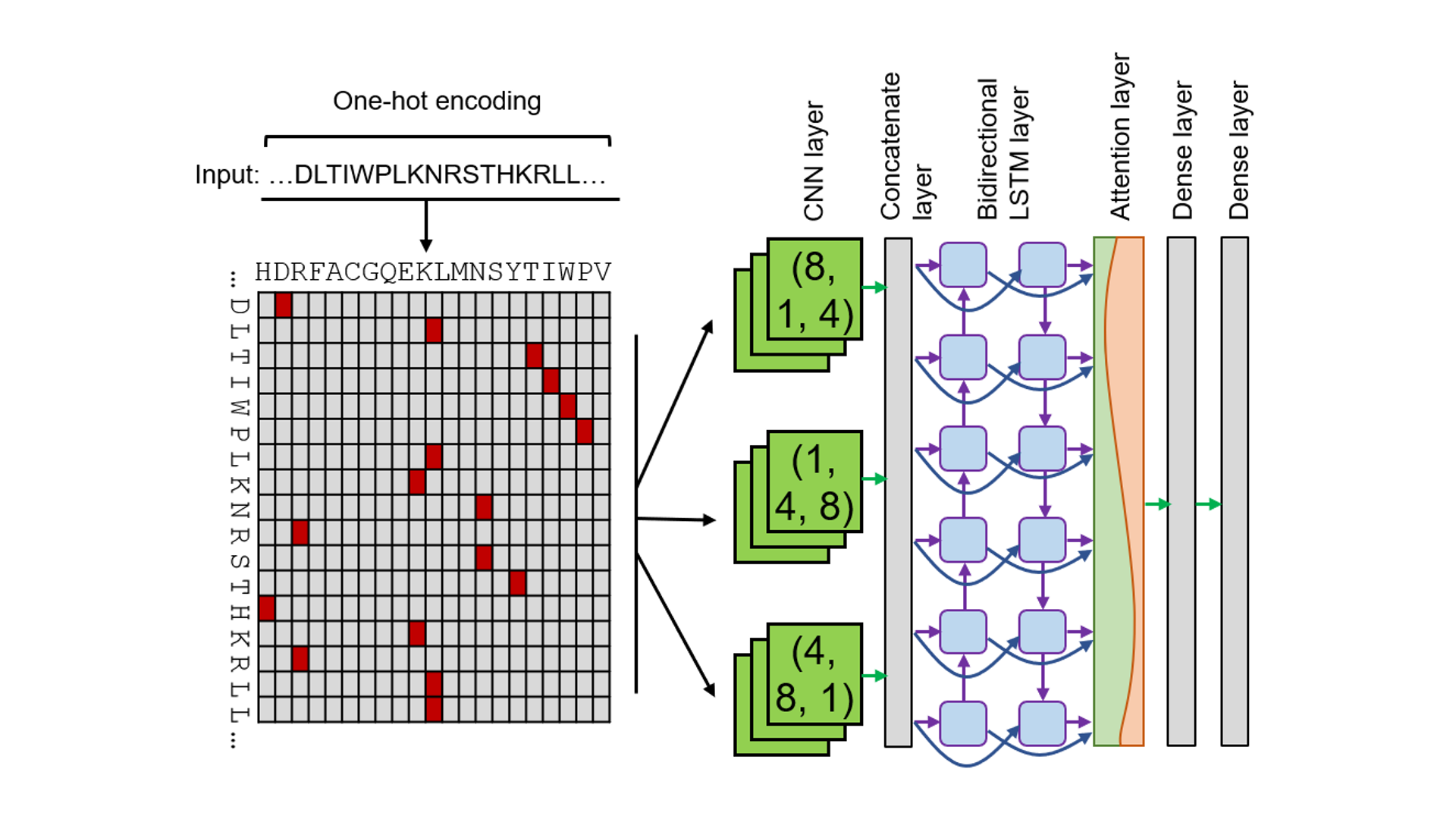
• The average cross validation AUC (20 times repeats) was 0.982.
• CNN-BiLSTM-Attention network structure achieved great performance.
• The combination of CNN layers with different convolution modes contributes to better performance.
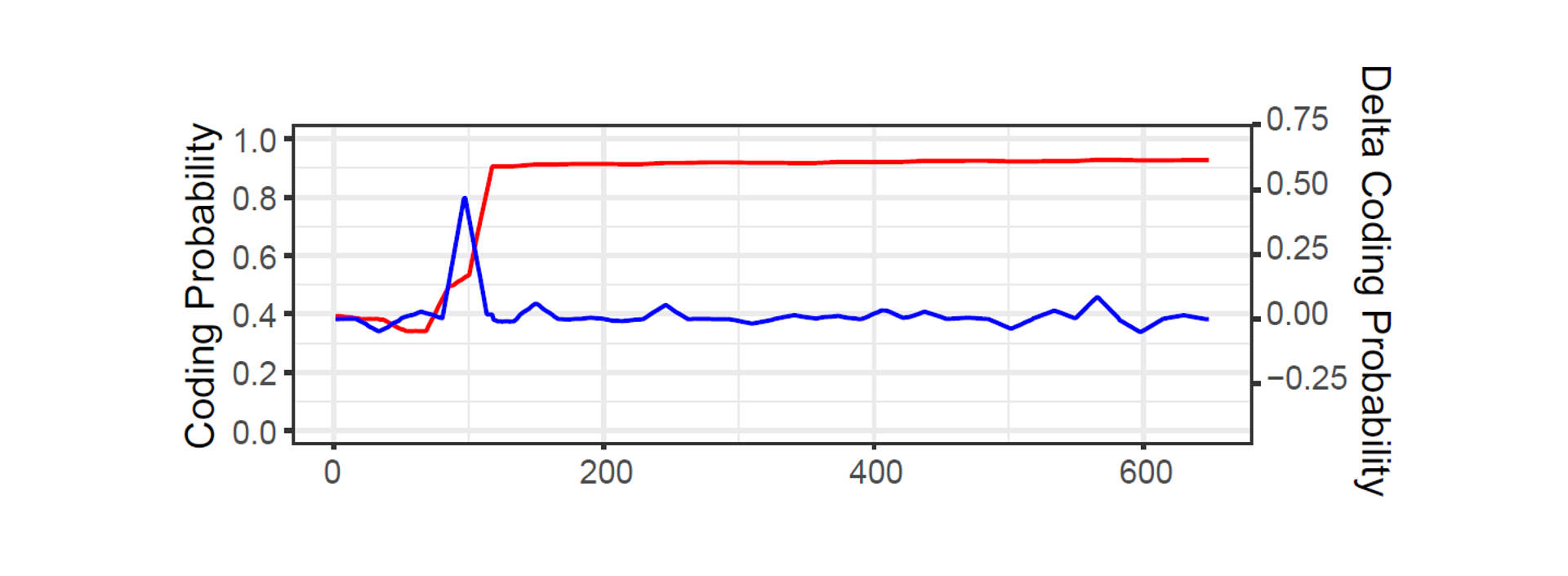
• We calculated the nuclear location probability trajectory for each protein.
• Based on the NLPT, we highlighted the delta score for each sites to indicate the importance of each sites.
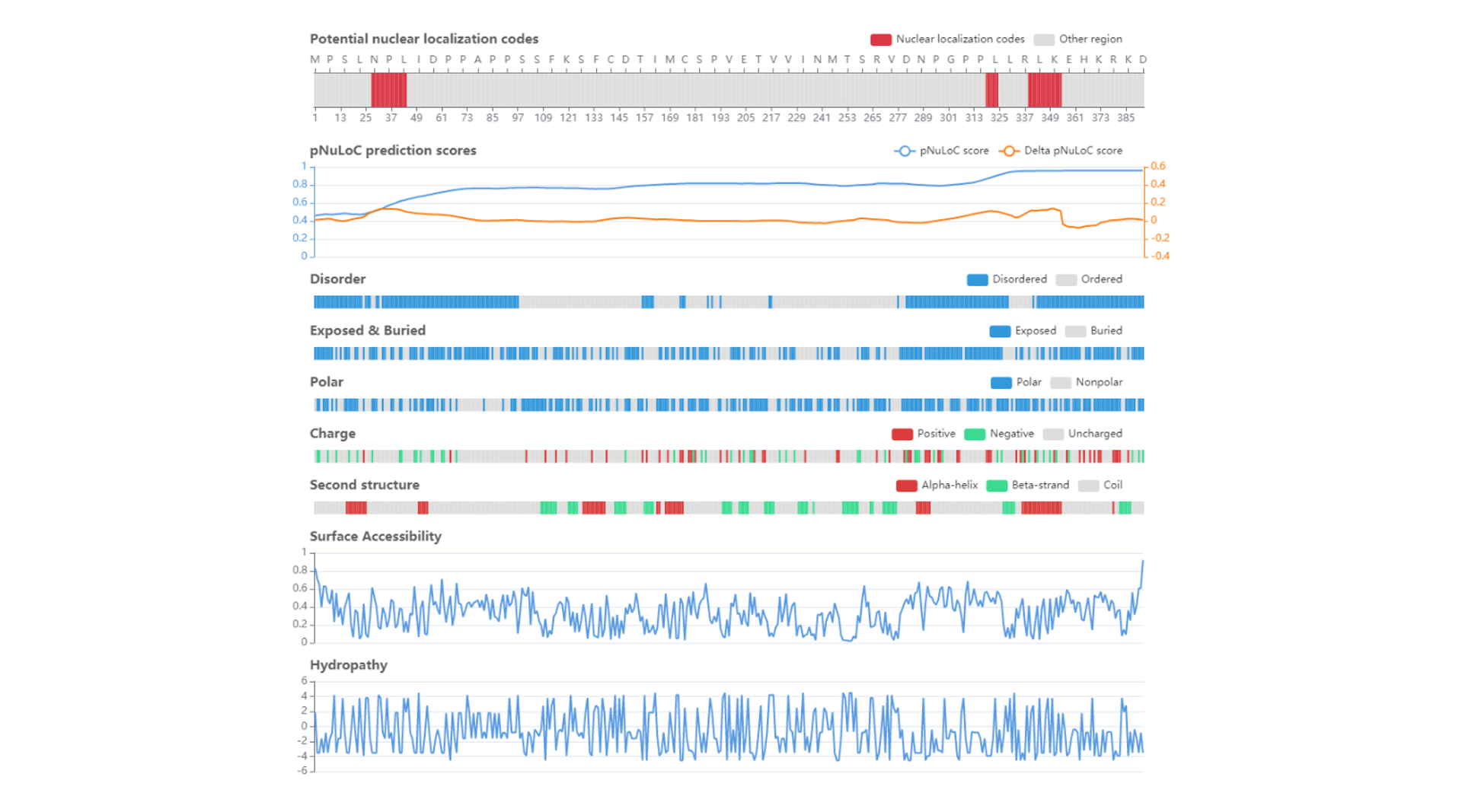
• The result page displayed the disorder region, surface accessibility, secondary structure, polar , charge and hydropathy of each query protein.
• The potential nuclear location regions of the query sequence are indicated.
